At MWC Shanghai 2023, a key theme was 时不我待, time waits for no-one, underlining the urgency of telcos’ search for new value
This key theme was underpinned three messages, echoed throughout the event. The first was the readiness of 5G to drive digital transformation in industry and enterprise. The second was importance of digital transformation to competitiveness and value creation, illustrated by multiple case studies at the event. The third focused on what 5G-Advanced could deliver.
Make 5G green and great
In the half decade since the launch of 5G, its ecosystem has matured and the tech has enabled new applications in consumer and enterprise markets. At the event Huawei showed off its its enhanced voice communications solution, 5G New Calling, for consumers which aims to provide a richer communications experience and generate higher margin revenue streams for operators. Another example of 5G in the consumer market is Fixed Wireless Access (FWA) which has brought reliable broadband to more homes.
5G is expected to build a new growth engine for operators with enterprise and industrial customers that will drive efficiency and value creation. There are already examples in manufacturing, mining and education.
Sustainability moves up the agenda
As 5G proliferates – in early 2023, the GSMA reported that there are more than 220 commercial 5G networks globally – sustainability and green practices have become dominant themes in telecoms. We need to optimise 5G networks’ performance, including power consumption, and at the event, network equipment vendors demonstrated their readiness to support CSPs’ sustainability goals. For example, China Mobile Zhejiang and Huawei launched their ‘0-bit, 0-Watt’ which permits network equipment to become deeply dormant.
To deliver network performance and sustainability necessitates implementing the latest innovations. At cell sites, telcos can ensure equipment is made of more eco-friendly and versatile materials that lasts longer in the field. For example, upgrading radio units to support multiple frequency bands requires fewer antennas.
Ensuring base station antennas ditch ungreen materials, such as those made from electroplating fibre glass, means more equipment can be recycled. As the amount of traffic a cell site handles steadily increases, CSPs are striving for equipment that can handle more traffic at the same or even lower levels of energy consumption. The latest Massive Multiple Input, Multiple Output (mMIMO) antennas can expand coverage areas without consuming more energy. The base station equipment must be as future-proof as possible.
New value creation cycle
Telecoms needs to harness the power of 5G in parallel with other technologies (such as AI, machine learning and robotics to continue digital transformation and help create greater value. The 3rd Generation Partnership Project’s (3GPP) Release 18, branded 5G-Advanced, is to be frozen by March 2024.
Figure 1: Timeline for 3GPP’s Release 18
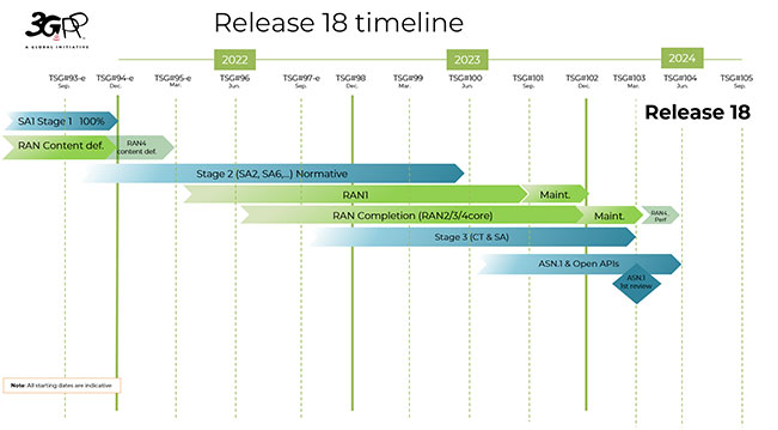
Source: 3GPP
This Release is intended to accommodate deeper integration of AI into the network and support new capabilities for a larger pool of use cases, such as 10Gbps connectivity, additional scenarios for IoT and integrated sensing and communication.
The jump to 10Gbps for peak downlink and 1Gbps for peak uplink could enable the immersive aspirations of the metaverse. The integration of sensing and communication is a milestone on the road to 6G and can deliver highly accurate positioning, localisation and more. Intelligence from sensors embedded within communications can also improve the communications’ performance. For example, enabling it to be more deterministic and offering more accurate assessments of channel conditions or using dynamic beam alignment for vehicle communications on mmWave.
5G-Advanced has the potential to expand the density of IoT deployment from 10 billion units to 100 billion through so-called passive IoT. This has been tested to improve performance, giving coverage a longer than existing technologies like radio frequency identification (RFID).
More hefty investment?
Will these next-generation capabilities in the mobile network force operators into another round of heavy investment? Not according to Huawei at MWC Shanghai 2023. The vendor will launch a portfolio of commercial 5G-Advanced network equipment next year. A key assurance was that the forthcoming 5G-Advanced solution will safeguard CSPs’ existing 5G investments and deliver better network performance simultaneously.
Huawei talked up products like the Extremely Large Antenna Array (ELAA) and AI-native technologies for 5G-Advanced core networks. The company has installed other key supporting technologies, such as Multi-Band Serving Cell (MBSC) and Flexible Spectrum Access (FSA), and said it working with more than 30 CSPs on technological verification and pilot projects for them.
ABI Research forecasts that by 2030, 5G-Advanced-based radio units will reach about 76 million and 23 million for macro basebands.
Figure 2: 5G-Advanced public network installed base by infrastructure type, world markets
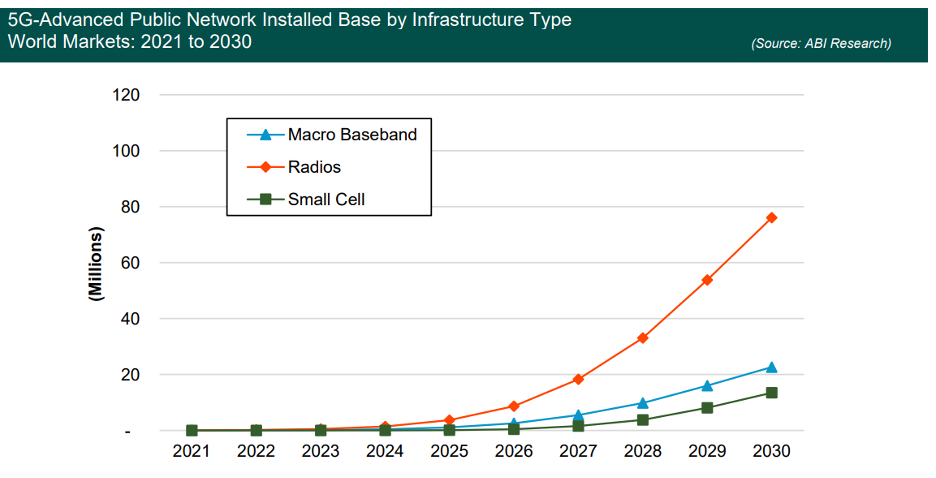
Source: ABI Research
Chinese CSPs are looking closely at the next-generation standard to continue innovating and maintain a competitive edge. China Mobile Hangzhou launched its Dual 10 Gigabit City project in early 2023 during the Asian Games. The project focuses on 5G-Advanced technologies to support applications like glasses-free, 3D experiences on different devices.
China Mobile Shanghai has a project to build the first 5G-Advanced intelligent 10 Gigabit Everywhere Everywhere City. The network will leverage the 2.6 GHz network initially for main urban areas before covering the whole of Shanghai.
Leveraging Innovation for Value Creation
At MWC Shanghai 2023, the maturity of 5G technology and the value 5G can deliver was very much in view. This message echoed through presentations by industry players and the exhibition floor. 5G has the potential to start greater convergence of multiple technologies throughout society but this trend requires a radically different approach to managing digital transformation as different technologies are needed to enable it. Nor will it be easy.
CSPs and enterprises need to implement a holistic, more systematic way of thinking and implementation to reap the benefits.
The signs are good. As 5G approaches its five-year mark, there are indicators that markets, firms and end users that implement the latest 5G technology will be more agile, have more robust communication, and greater intelligence in the network than those that do not.
5G SA provides upgrades to network core, but 5G-Advance can fully integrate the 5G core, 5G RAN, cloud-native and microservices to enable allow a diverse range of services for consumers and enterprises.
About the Author: Dean Tan, Industry Analyst, is a member of ABI Research’s Asia-Pacific team. He contributes to various research projects, from operators’ strategies incluidng monetisation, to mobile network infrastructure, and wireless applications and use cases.
About ABI Research
ABI Research is a global technology intelligence firm delivering actionable research and strategic guidance to technology leaders, innovators, and decision makers around the world. Its research focuses on transformative technologies that are reshaping industries, economies, and workforces today. www.abiresearch.com


